The last post started implementing our new demo application - the movie library. We were forced to introduce a React class component with state to make the search form work.
When we type in the search text box and submit the form the expected action is sent to the redux store, as you can see in this screenshot featuring redux-devtools-extension.
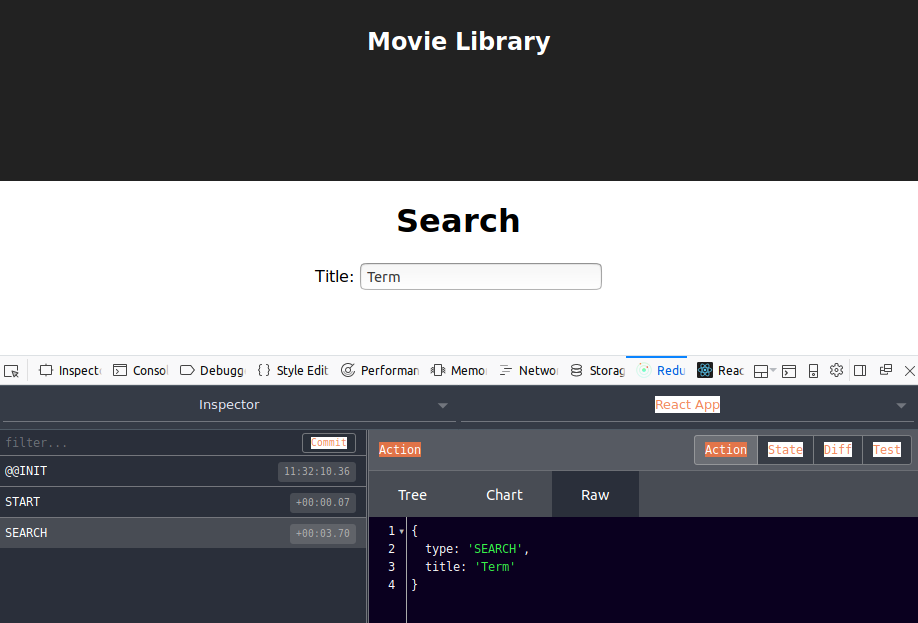
Routing
For this example we are going to use redux-first-router. As mentioned previously redux-first-router binds routes to actions. We must handle those actions and update the UI accordingly.
See the redux-router documentation for the full documentation, but we need to make index.js look like this:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
import registerServiceWorker from './registerServiceWorker';
import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import { connectRoutes } from 'redux-first-router';
import createHistory from 'history/createBrowserHistory';
import App from './App';
import {searchReducer} from './Search';
const routesMap = {
HOME: '/'
};
const { reducer, middleware, enhancer } = connectRoutes(createHistory(), routesMap)
const store = createStore(combineReducers({
location: reducer,
search: searchReducer
}), compose(enhancer, applyMiddleware(middleware),
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()));
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root'));
store.dispatch({type: "START"});
registerServiceWorker();
routesMap defines the mapping between action types and routes. Here we are saying that the route / should map to the HOME action type. The redux-first-router state is put into the store on the location key.
Next we connect the App component to the Redux store:
function App({type}) {
const componentMap = {
HOME: ConnectedSearch
};
const View = componentMap[type];
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<h1 className="App-title">Movie Library</h1>
</header>
<View />
</div>
);
}
export default connect(function mapStateToProps(state) {
return state.location;
},
(dispatch) => ({}))(App);
redux-first-router puts route information into the redux store when a route is matched. mapStateToProps extracts the location key from the store, which is then used in the App component to extract the type value.
componentMap maps route action types to React components. If the route action type is HOME then View will be a ConnectedSearch, which is what we want for the home page.
AJAX Actions
The difficulty we encounter when trying to search for a movie (via an AJAX request) is that we can’t take the search action ({ type: "SEARCH", title: "Term" }) and update the UI state from that. We need to make an asynchronous request in the middle.
Nearly every React application must overcome this difficulty. There are lots of different solution and I will present one.
First, install redux-promise-middleware.
$ npm install redux-promise-middleware --save
redux-promise-middleware is a library that intercepts actions that carry a promise (SEARCH). When the promise resolves the library dispatches a new action with the result (SEARCH_FULFILLED).
We create a promise using the fetch API to make a request to omdbapi to search for movies by title.
We dispatch:
dispatch({
type: 'SEARCH',
payload: fetch(`http://www.omdbapi.com/?apikey=8e4dcdac&s=${encodeURIComponent(title)}`)
.then((response) => response.json())
});
and in the reducer look for SEARCH_FULFILLED:
export function searchReducer(state = {results: []}, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "SEARCH_FULFILLED":
return Object.assign(
{},
{ results: action.payload.Response
? action.payload.Search.filter(({Poster}) => Poster !== "N/A")
: []});
default: return state;
}
}
Update the Search component to display our recently acquired movie data:
function Search({ onSearch, results = [] }) {
return <div>
<h1>Search</h1>
<SearchForm onSearch={onSearch} />
<div>
{results.map(({Title,Poster,imdbID})=>
<img src={Poster} alt={Title} key={imdbID} />)}
</div>
</div>;
}
Now look at our amazing application!
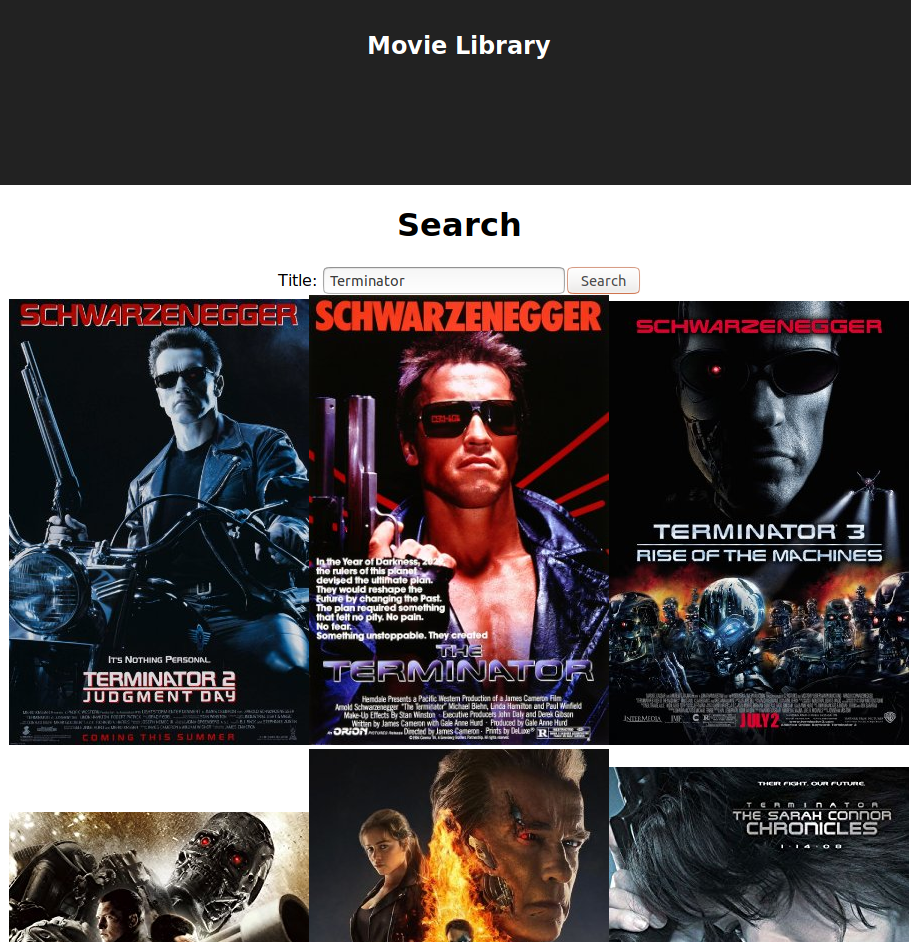
The complete Search.js is:
import React from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
class SearchForm extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {title: ""}
this.titleChange = this.titleChange.bind(this);
this.search = this.search.bind(this);
}
titleChange(event) {
this.setState({title: event.target.value});
}
search(event) {
event.preventDefault();
this.props.onSearch(this.state.title);
}
render() {
return <div><form onSubmit={this.search}>
<label htmlFor="title">Title: </label>
<input type="text" name="title" value={this.state.title} onChange={this.titleChange}/>
<input type="submit" value="Search"/>
</form>
</div>;
}
}
function Search({ onSearch, results = [] }) {
return <div>
<h1>Search</h1>
<SearchForm onSearch={onSearch} />
<div>
{results.map(({Title,Poster,imdbID})=> <img src={Poster} alt={Title} key={imdbID} />)}
</div>
</div>;
}
export const ConnectedSearch = connect(
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return state.search;
},
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {
onSearch: (title)=> {
dispatch({
type: 'SEARCH',
payload: fetch(`http://www.omdbapi.com/?apikey=8e4dcdac&s=${encodeURIComponent(title)}`)
.then((response) => response.json())
});
}
};
}
)(Search);
export function searchReducer(state = {results: []}, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "SEARCH_FULFILLED":
return Object.assign(
{},
{ results: action.payload.Response
? action.payload.Search.filter(({Poster}) => Poster !== "N/A")
: []});
default: return state;
}
}
Summary
First, we setup redux-first-router and implemented the HOME route. Then we introduced redux-promise-middleware as a way of inserting asynchronous operations into the redux data cycle.
Get The Code
The code for this example is on Github. You can access the code as it was at the completion of this step by cloning the repository and checking out the tag that corresponds to this post.
git clone https://github.com/liammclennan/movie-library.git
git checkout react8
or browse at https://github.com/liammclennan/movie-library/tree/c93c652fa1318ce6447d985e3f8b690386456565.